Link Technologies - LinkSOFT Documentation
Link Technologies - LinkSOFT Documentation  Link Technologies - LinkSOFT Documentation
Link Technologies - LinkSOFT Documentation Processing Depreciation will create a Depreciation Entry for all assets that are in the range specified. The following criteria must be met for an Asset to be Depreciated.
Asset STATUS is Active .
Asset has not been depreciated for the period selected.
Account codes specified for the asset is a valid account in the General Ledger system.
To calculate depreciation select the following: Refer to Figure 1 below.
| Task | Description |
| 1 | Select the Depreciation Date - up to the date you want to process Depreciation for the Asset. |
| 2 | Select Asset . |
| 3 | Select Group . |
| 4 | Select Classification . Depreciation Rules are attached to the Classification and Classification are attached to Assets hence asset will be depreciated depending on the depreciation rule. |
| 5 | Select Location . |
| 6 | Select Validate . |
| 7 | Select Depreciate. |
Note:
There are 3 phases of depreciation.
When the depreciation is added on the system , it processes to create a new batch with status "In Progress", this is where system starts to validate the depreciation. Refer to Figure 2 below.
When validation is successfully completed, system starts to depreciate the assets where status is "In Progress". Refer to Figure 3 below.
Once depreciation calculations have been completed, then the journal entries are created on the system. Refer to Figure 4 below.
When the journals have been successfully created and the depreciated is marked as completed then journals are reflected in the financial system. Refer to Figure 5 below.
The System Setting determines the General Ledger Code used when an Asset is Depreciated.
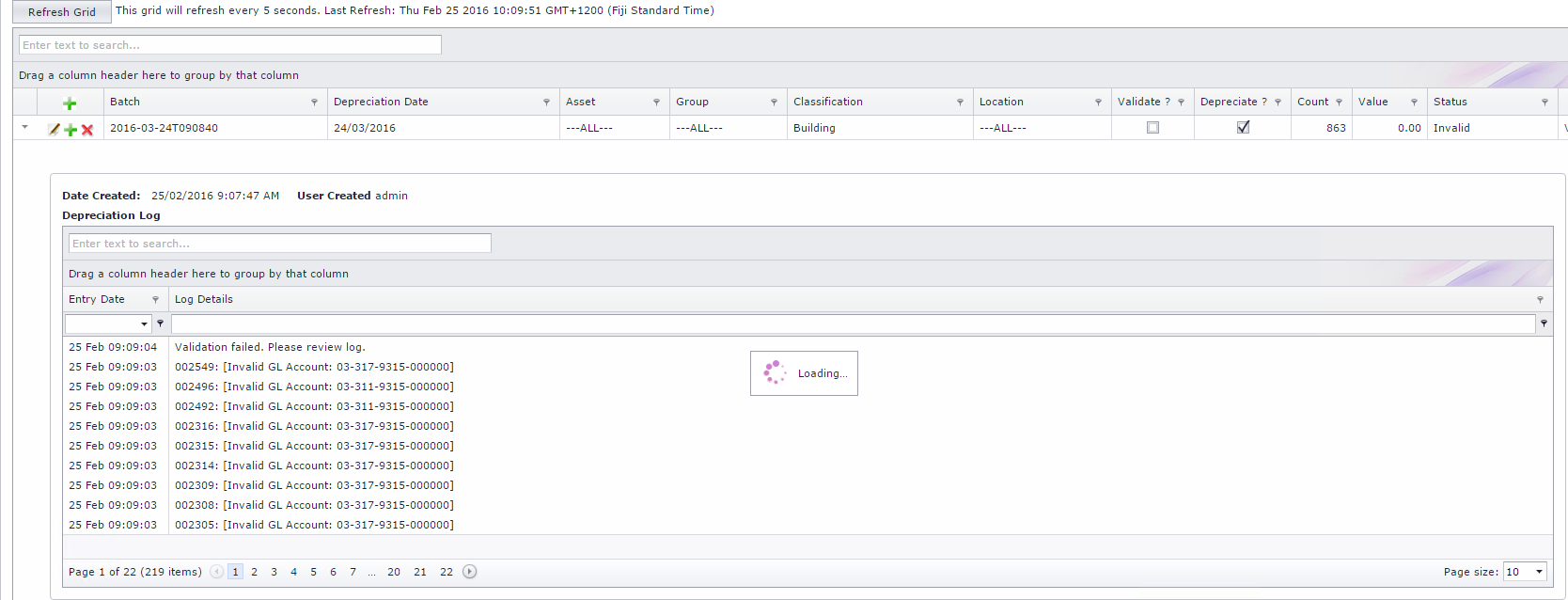
If any of the Account Codes are invalid, the depreciation process will not run. You need to resolve any Invalid Account Code issues before processing a Depreciation. The status of the depreciation will read Invalid, where the details can be viewed under the Depreciation Log. Click on the grey triangle next to the depreciation entry to view the log. Refer to Figure 6 Below.
Depreciation Calculations:
The calculation of Depreciation is dependent on the following factors:
Cost - the original cost of the asset. This cost may include Installation Costs, Taxes, and any other costs of putting the asset into service.
Salvage value - the estimated value of the asset at the end of its useful life.
Prior Accumulated Depreciation - this is the amount of depreciation that had been expensed for the asset before entry into the Asset Manager. The methodology used to calculate any previous depreciation may produce a slightly different amount than what
Life - the estimated useful life of the asset.
Formula:
Straight Line Depreciation : For an asset that is newly entered into the Asset Manager, the calculation for straight line depreciation is:
|
(cost - salvage value) / Life of the Asset |
Declining Balance Depreciation : The declining balance method calculates higher depreciation charges at the beginning of an asset's useful life. Depreciation value reduces in sub-sequent years.
Each year, the depreciation is calculated using the same constant percentage rate. In the first year, the system calculates the depreciation based on the asset's acquisition cost. In the following years, the calculation is based on the asset's remaining book value.
Examples of depreciation calculations is available to view on this spreadsheet.
Figure 1: Form to create a new depreciation entry
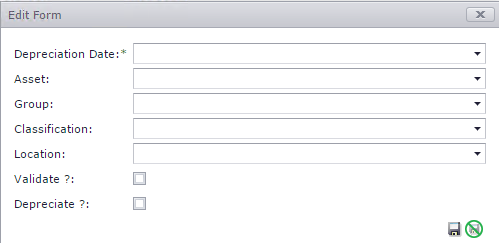
Figure 2: Form to view depreciation log which will show the progress and any messages relating to depreciation calculations
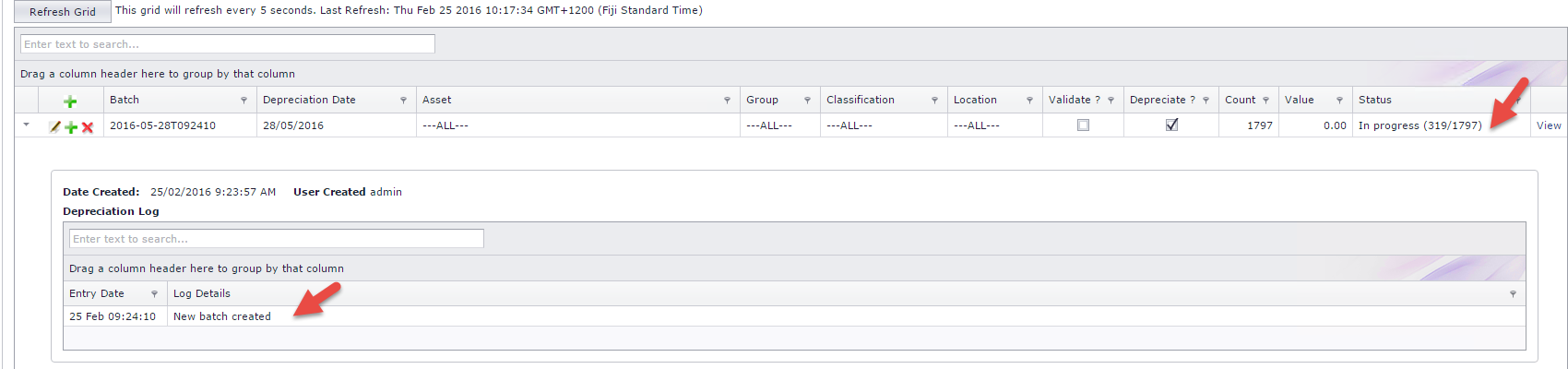
Figure 3: Depreciation Validation Process
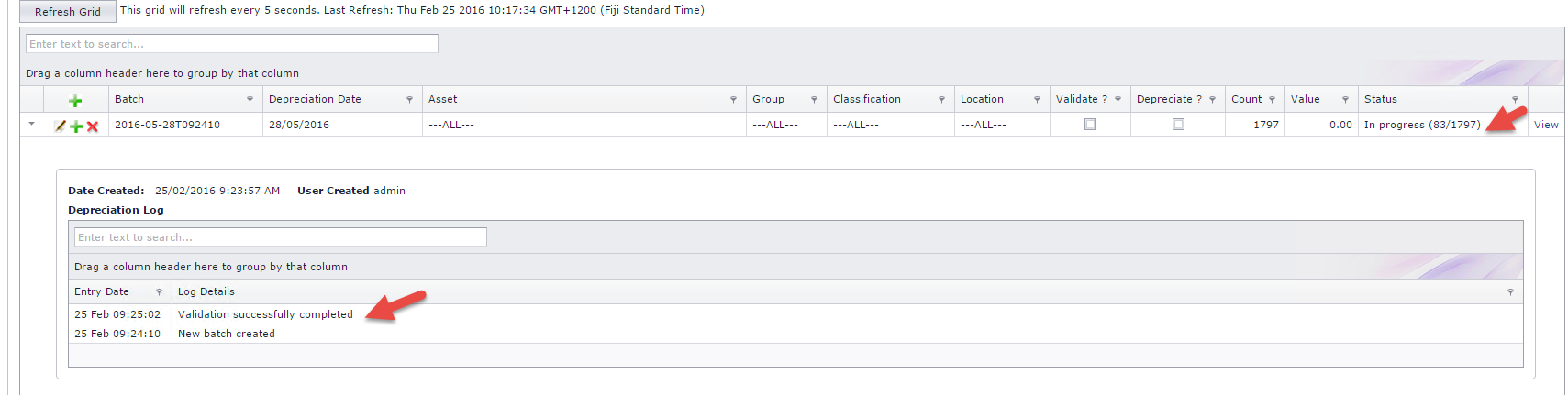
Figure 4: Journal creation after Depreciation Process

Figure 5: Depreciation Completed and Journals Posted
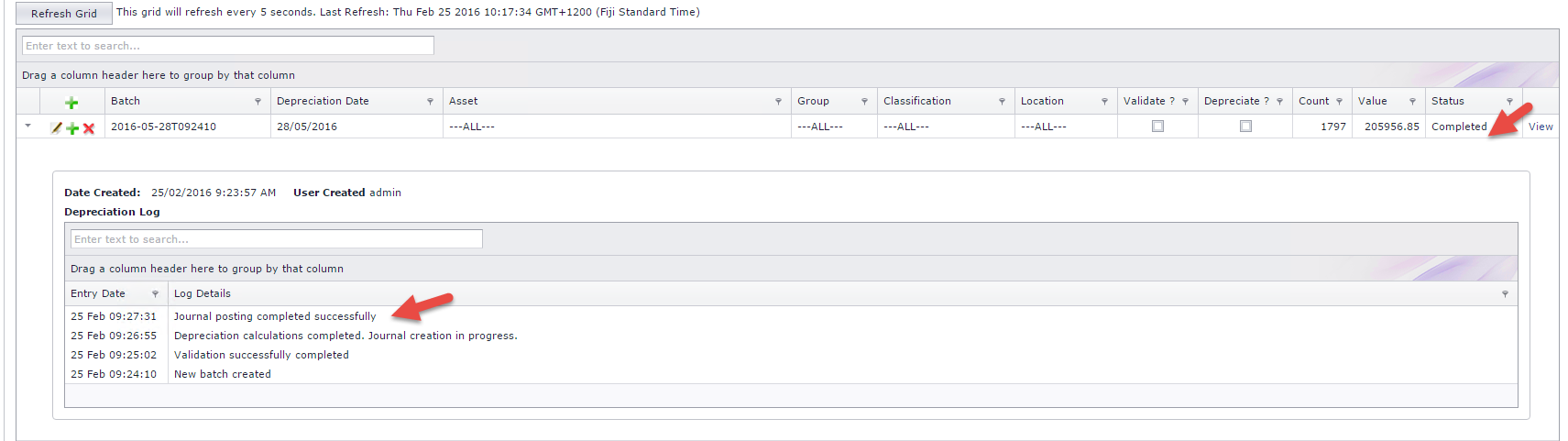
Figure 6: Invalid GL Accounts